Authors:
(1) Moritz Jasper, Barkhausen Institut gGmbH, Wurzburger Straße 46, Dresden, Germany ([email protected]);
(2) Stefan Kopsell, Barkhausen Institut gGmbH, Wurzburger Straße 46, Dresden, Germany ([email protected]).
Table of Links
Attacker Model and Security Goals
VI. IMPLEMENTATION AND EVALUATION
An implementation of LCMsec is publicly available[2]. It is written in C++ and uses the Botan[3] cryptography library. In the implementation of the Dutta Barua protocol, we use a modified version based on elliptic curve cryptography for performance reasons.
A. Latency and Throughput
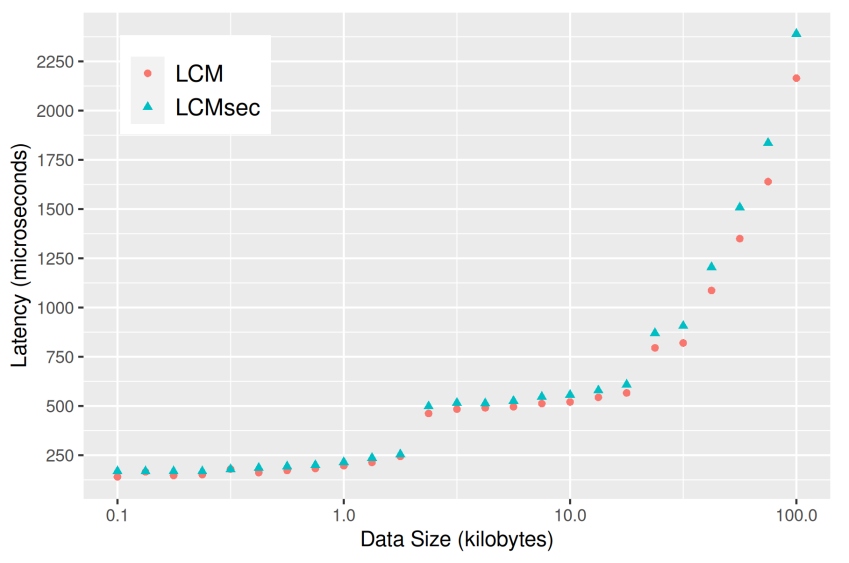
Latency and throughput of the LCMsec protocol were tested using two identical servers with an Intel Xeon Gold 5317 processor and 8GB RAM running Linux 5.15. The servers were one hop apart with a 1GBit/s link between them. To test the latency of LCMsec messages, an echo test was performed: one of the servers, the source, transmitted messages of sizes ranging from 100 Bytes to 100 Kilobytes. Upon receiving one of these messages, the other server immediately re-transmitted it. Upon receiving the original message back, the latency was measured by the source. For each message size, a total of 1000 latency measurements were taken. The same was done for the original LCM library. The results are depicted in Figure 8 – as one can see, there is only a small latency overhead. Note that the jump at 3 KB is due to fragmentation of the LCM messages, which occurs at that size.
To measure the throughput achieved by LCMsec, a similar echo test was performed on the same servers. Using a fixed message size, the source increased the bandwidth at which it transmitted while recording the number of messages it received back. In such a test, the percentage of lost messages can indicate the throughput capabilities of LCMsec. However, no difference between LCM and LCMsec was observed: in both cases, no messages were lost up to a bandwidth of 123MB/s. After this point, a majority of messages were dropped since the limit of the link between the servers had been reached.
B. Evaluation of the Group Discovery
The most expensive part of the group discovery are the JOIN Responses: They may be large since they contain the certificates of all other users. Thus, the number of JOIN Responses needed should be kept to a minimum. To evaluate the performance of the protocol, measuring the time taken to perform the group discovery protocol is not helpful, since it is bounded by timeouts. Instead, we count the number of JOINs and JOIN_Responses transmitted while a varying number of nodes execute the group discovery protocol and subsequent DBGKA twice (in order to agree on both kg and kch).
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
[2] https://github.com/Barkhausen-Institut/lcm-sec
[3] https://botan.randombit.net/

